基于GBRWT的压缩感知磁共振图像重建 (中文,English)
赖宗英1,2, 屈小波2,*, 刘运松2, 郭迪3, 叶婧2, 占志芳2, 陈忠2,*
1厦门大学通信工程系、电子科学系,福建等离子体与磁共振重点研究实验室,中国,厦门,361005;
2厦门大学电子科学系,福建等离子体与磁共振重点研究实验室,中国,厦门,361005;
3厦门理工学院,计算机与信息工程学院,中国厦门,361024。
联系人: 屈小波 quxiaobo<|at|>xmu.edu.cn
引用:
Zongying Lai#, Xiaobo Qu#, Yunsong Liu, Di Guo, Jing Ye, Zhifang Zhan, Zhong Chen. Image reconstruction of compressed sensing MRI using graph-based redundant wavelet transform, Medical Image Analysis, 27: 93-104, 2016. (# denotes co-first authorship)
全文: http://authors.elsevier.com/a/1S1Ie4rfPllVGc (50天内免费)
代码:(http://csrc.xmu.edu.cn/project/CS_MRI_GraphWavelet/Toolbox_GBRWT_MRI.zip)
摘要:
压缩感知磁共振成像技术利用磁共振图像在特定变换域上的稀疏性,用低于奈奎斯特采样率的数据重建高质量的磁共振图像来达到加速成像的目的。稀疏表示的性能对加速成像的倍数以及相同加速倍数下重建图像的质量起着至关重要的作用。本文将图像块表示成图论中的顶点和图像块之间的差异表示顶点距离,利用参考图像找寻图上的最小距离,然后对像素进行排序和冗余小波变换,得到一种基于图的冗余小波变换(Graph based redundant wavelet transform, GBRWT)。以GBRWT 作为稀疏变换,本文结合压缩感知磁共振成像的方法,用1-范数来约束系数的稀疏性,对欠采样的磁共振信号进行稀疏迭代重建。仿真结果表明:GBRWT在欠采样条件下能较好的重建目标图像。与现有的前沿技术比较,本文的方法能更好的去除伪影,保留图像的边沿细节信息。
关键词: 压缩感知,图,小波变换,磁共振成像,图像重建
方法:
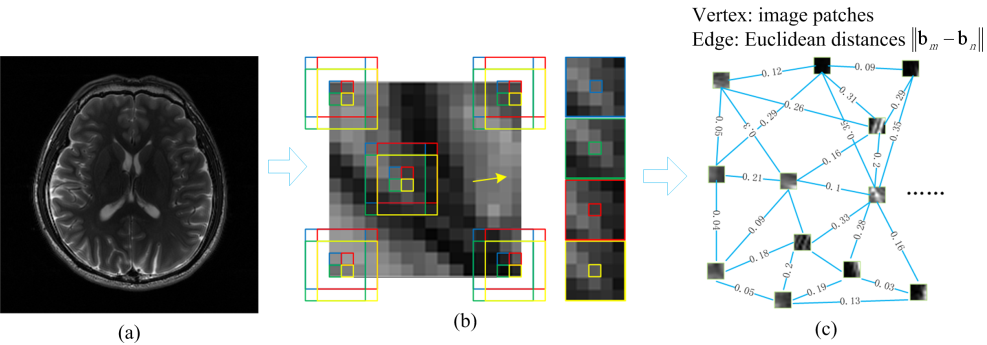
GBRWT首先是将图像分为相互有重叠的图像块,将这些图像块作为图的顶点,图像块互相连接。以图像块之间的相似性(2范数误差)作为连接(边)的权重建立图。用类似邮差问题的方法找到一条每个顶点只访问一次的最短路径(排列顺序),使得相邻顶点之间的相似性得以保证,也就是说:新的排序使得图像像素排列更光滑。然后进行冗余小波变换将得到稀疏的变换系数。图1 是图像分块及用图像块组建图的示意图。图2 是基于GBRWT的压缩感知磁共振图像欠采样及重建的流程图。

图 1 基于图像块组建图的示意图。
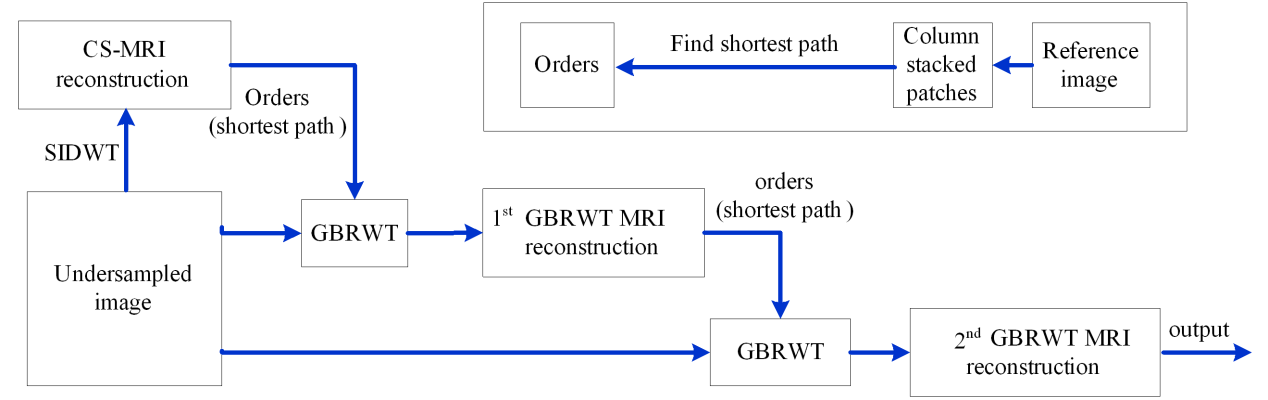
图 2 基于GBRWT的压缩感知磁共振图像重建流程图。
实验结果:
1. 人造模型数据仿真
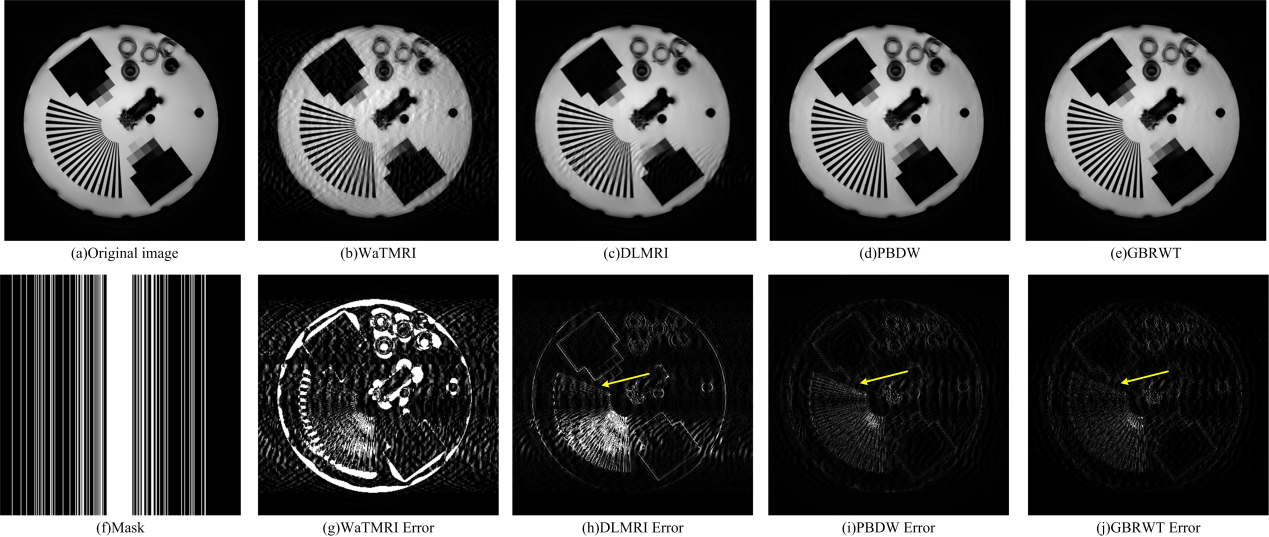
图 3 模型数据(采样率为27%)的欠采样重建结果和残差。(a) 全采样图像; (b-e)分别是基于WaTMRI, DLMRI, PBDW 和GBRWT的重建结果;(f) 欠采样模板;(g-j)残差图(´5)
2. 活体数据仿真

图 4 2D随机欠采(采样率为20%)时的重建图像及残差。(a) 全采样图像; (b-e)分别是基于WaTMRI, DLMRI, PBDW 和 GBRWT的重建图像;(f) 欠采样模板; (g-j) 残差图(´5).

图5 卡迪尔坐标系(采样率为31%)时的重建图像及残差。 (a) 全采样图像; (b-e)分别是基于WaTMRI, DLMRI, PBDW 和 GBRWT的重建图像;(f) 欠采样模板; (g-j) 残差图(´5).

图 6 重建误差比较:PBDW和GBRWT的参考图像都是基于SIDWT欠采样重建得到的图像。.
结论
本文介绍了一种基于(graph-based redundant wavelet transform, GBRWT)稀疏变换和压缩感知的磁共振图像欠采样重建方法。GBRWT是通过采用图的结构和寻找图像像素新的排序使得像素排列更加光滑,对光滑信号进行小波变换形成新的稀疏表示。由于GBRWT变换的系数更稀疏,磁共振图像欠采样重建的效果得以改善。本文的方法与现有的前沿技术PBDW、DLMRI以及WaTMRI比较的结果表明,本文方法重建的图像与全采样图像在亮度和细节信息上都具有更好的一致性。由于小波变换对光滑的信号变换,其系数更稀疏。改善图像像素的排序方法能使得GBRWT的稀疏表示能力更深入,从而改进图像的重建效果。同时,也可以采用并行计算来加快重建时间。
参考文献:
[1]. Aelterman, J., Luong, H.Q., Goossens, B., Pižurica, A., Philips, W., 2011. Augmented Lagrangian based reconstruction of non-uniformly sub-Nyquist sampled MRI data. Signal Processing 91, 2731-2742.
[2]. Aharon, M., Elad, M., Bruckstein, A., 2006. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54, 4311-4322.
[3]. Akcakaya, M., Basha, T.A., Chan, R.H., Rayatzadeh, H., Kissinger, K.V., Goddu, B., Goepfert, L.A., Manning, W.J., Nezafat, R., 2012. Accelerated contrast-enhanced whole-heart coronary MRI using low-dimensional-structure self-learning andthresholding. Magn. Reson. Med.67, 1434-1443.
[4]. Akcakaya, M., Basha, T.A., Goddu, B., Goepfert, L.A., Kissinger, K.V., Tarokh, V., Manning, W.J., Nezafat, R., 2011. Low-dimensional-structure self-learning and thresholding: regularization beyond compressed sensing for MRI reconstruction. Magn.Reson. Med.66, 756-767.
[5]. Akcakaya, M., Basha, T.A., Pflugi, S., Foppa, M., Kissinger, K.V., Hauser, T.H., Nezafat, R., 2014. Localized spatio-temporal constraints for accelerated CMR perfusion. Magn. Reson. Med.72, 629-639.
[6]. Baker, C.A., King, K., Dong, L., Leslie, Y., 2011. Translational-invariant dictionaries for compressed sensing in magnetic resonance imaging, 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 1602-1605.
[7]. Baraniuk, R., Choi, H., Neelamani, R., Ribeiro, V., Romberg, J., Guo, H., Fernandes, F., et.al, 2011. http://dsp.rice.edu/software/rice-wavelet-toolbox.
[8]. Chaari, L., Pesquet, J.C., Benazza-Benyahia, A., Ciuciu, P., 2011. A wavelet-based regularized reconstruction algorithm for SENSE parallel MRI with applications to neuroimaging. Med. Image Anal.15, 185-201.
[9]. Chang, C.H., Ji, J., 2010. Improved compressed sensing MRI with multi-channel data using reweighted l(1) minimization, 2010 Annual International Conference Of the IEEE Engineering In Medicine And Biology Society, 875-878.
[10]. Chen, C., Huang, J.Z., 2014. The benefit of tree sparsity in accelerated MRI. Med. Image Anal.18, 834-842.
[11]. Chen, Y.M., Ye, X.J., Huang, F., 2010. A novel method and fast algorithm for MR image reconstruction with significantly under-sampled data. Inverse Probl. Imaging 4, 223-240.
[12]. Cormen, T.H., Leiserson, C.E., Rivest, R.L., Stein, C., 2001. Introduction to algorithms. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England.
[13]. Daubechies, I., Defrise, M., De Mol, C., 2004. An iterative thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems with a sparsity constraint. Commun. Pur. Appl. Math.57, 1413-1457.
[14]. Greiser, A., von Kienlin, M., 2003. Efficient k-space sampling by density-weighted phase-encoding. Magn. Reson. Med. 50, 1266-1275.
[15]. Huang, F., Lin, W., Duensing, G.R., Reykowski, A., 2012. k-t sparse GROWL: Sequential combination of partially parallel imaging and compressed sensing in k-t space using flexible virtual coil. Magn. Reson. Med.68, 772-782.
[16]. Jacob, M., 2009. Optimized non-uniform fast Fourier transform (NUFFT) for iterative tomographic reconstruction, 2009. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 673-676.
[17]. Jim, J., Zhi-Pei, L., 2001. High resolution cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: a model-based approach, 2001. Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2268-2271.
[18]. Junfeng, Y., Yin, Z., Wotao, Y., 2008. A fast TVL1-L2 minimization algorithm for signal reconstruction from partial Fourier data. CAAM 09-24,Rice university.
[19]. Junfeng, Y., Yin, Z., Wotao, Y., 2010. A fast alternating direction Method for TVL1-L2 signal reconstruction from partial fourier data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process.4, 288-297.
[20]. Khalidov, I., Fadili, J., Lazeyras, F., Van De Ville, D., Unser, M., 2011. Activelets: Wavelets for sparse representation of hemodynamic responses. Signal Processing 91, 2810-2821.
[21]. Liu, Y, Cai, J-F, Zhan, Z, Guo, D, Ye, J, Chen, Z., Qu, X., 2015. Balanced sparse model for tight frames in compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS ONE 10. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119584.
[22]. Lustig, M., Donoho, D.L., M.Santos, J., Pauly, J.M., 2008. Compressed sensing MRI. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 72, 72-82.
[23]. Maggioni, M., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K., Foi, A., 2013. Nonlocal transform-domain filter for volumetric data denoising and reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22, 119-133.
[24]. Majumdar, A., Ward, R.K., 2011. An algorithm for sparse MRI reconstruction by Schatten p-norm minimization. Magn. Reson. Imaging 29, 408-417.
[25]. Majumdar, A., Ward, R.K., 2012. Causal dynamic MRI reconstruction via nuclear norm minimization. Magn. Reson. Imaging 30, 1483-1494.
[26]. Majumdar, A., Ward, R.K., Aboulnasr, T., 2013. Non-convex algorithm for sparse and low-rank recovery: Application to dynamic MRI reconstruction. Magn. Reson. Imaging 31, 448-455.
[27]. Ning, B., Qu, X., Guo, D., Hu, C., Chen, Z., 2013. Magnetic resonance image reconstruction using trained geometric directions in 2D redundant wavelets domain and non-convex optimization. Magn. Reson. Imaging 31, 1611-1622.
[28]. Qu, X., Guo, D., Ning, B., Hou, Y., Lin, Y., Cai, S., Chen, Z., 2012. Undersampled MRI reconstruction with patch-based directional wavelets. Magn. Reson. Imaging 30, 964-977.
[29]. Qu, X., Hou, Y., Lam, F., Guo, D., Zhong, J., Chen, Z., 2014. Magnetic resonance image reconstruction from undersampled measurements using a patch-based nonlocal operator. Med. Image Anal. 18, 843-856.
[30]. Qu, X., Zhang, W., Guo, D., Cai, C., Cai, S., Chen, Z., 2010. Iterative thresholding compressed sensing MRI based on contourlet transform. Inverse Probl. Sci. En. 18, 737-758.
[31]. Ram, I., Elad, M., Cohen, I., 2011. Generalized tree-based wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59, 4199-4209.
[32]. Ram, I., Elad, M., Cohen, I., 2012. Redundant wavelets on graphs and high dimensional data clouds. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19, 291-294.
[33]. Ram, I., Elad, M., Cohen, I., 2013. Image processing using smooth ordering of its patches. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22, 2764-2774.
[34]. Ravishankar, S., Bresler, Y., 2011. MR image reconstruction from highly undersampled k-space data by dictionary learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30, 1028-1041.
[35]. Shensa, M., 1992. The discrete wavelet transform: wedding the atrous and Mallat algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40, 2464-2482.
[36]. Singh, G., Raj, A., Kressler, B., Nguyen, T.D., Spincemaille, P., Zabih, R., Wang, Y., 2011. A fast edge-preserving bayesian reconstruction method for parallel imaging applications in cardiac MRI. Magn. Reson. Med.65, 184-189.
[37]. Skiena, S.S., 2008. The algorithm design manual. Springer, London.
[38]. Tsai, C.M., Nishimura, D.G., 2000. Reduced aliasing artifacts using variable-density k-space sampling trajectories. Magn. Reson. Med. 43, 452-458.
[39]. Wang, Y.-H., Qiao, J., Li, J.-B., Fu, P., Chu, S.-C., Roddick, J.F., 2014. Sparse representation-based MRI super-resolution reconstruction. Measurement 47, 946-953.
[40]. Wang, Y., Ying, L., 2014. Compressed sensing dynamic cardiac cine MRI using learned spatiotemporal dictionary. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61, 1109-1120.
[41]. Weller, D.S., Polimeni, J.R., Grady, L., Wald, L.L., Adalsteinsson, E., Goyal, V.K., 2011. Combined compressed sensing and parallel mri compared for uniform and random Cartesian undersampling of k-space, 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 553-556.
[42]. Weller, D.S., Polimeni, J.R., Grady, L., Wald, L.L., Adalsteinsson, E., Goyal, V.K., 2013. Sparsity-promoting calibration for GRAPPA accelerated parallel MRI reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32, 1325-1335.
[43]. Xiuquan, J., Jingfei, M., Aref, M., Wiener, E., Zhi-Pei, L., 2003. An improved MRI method for dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging of tumors, 2003. Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 478-481.
[44]. Ying, D., Ji, J., 2011. Compressive sensing MRI with laplacian sparsifying transform, 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 81-84.
[45]. Yue, H., Lingala, S.G., Jacob, M., 2012. A fast majorize-minimize algorithm for the recovery of sparse and low-rank matrices. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21, 742-753.
[46]. Yue, H., Paisley, J., Qin, L., Xinghao, D., Xueyang, F., Xiao-Ping, Z., 2014. Bayesian nonparametric dictionary learning for compressed sensing MRI. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23, 5007-5019.
[47]. Zhang, S.T., Zhan, Y.Q., Dewan, M., Huang, J.Z., Metaxas, D.N., Zhou, X.S., 2012. Towards robust and effective shape modeling: Sparse shape composition. Med. Image Anal. 16, 265-277.
[48]. Zhou, W., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P., 2004. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13, 600-612.