多对比度图像graph稀疏学习下的磁共振图像稀疏重建(英文版)
赖宗英1,2, 屈小波2,*, 鲁恒发2, 彭玺3, 郭迪4, 杨钰2, 郭岗5, 陈忠2,*
1厦门大学,通信工程系,中国,厦门,361005;
2厦门大学,电子科学系,福建等离子体与磁共振重点研究实验室,中国,厦门,361005;
3中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院医工所劳特伯生物医学成像研究中心,中国,深圳,518055;
4厦门理工学院,计算机与信息工程学院,中国,厦门,361024;
5厦门第二医院,放射科,中国,厦门,361021。
引用: Zongying
Lai, Xiaobo Qu, Hengfa Lu, Xi Peng, Di Guo, Yu Yang, Gang Guo, Zhong Chen. Sparse
MRI reconstruction using multi-contrast image guided graph representation, Magnetic Resonance
Imaging, 43:95-104, 2017.
全文: (
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2017.07.009)
代码: ( https://csrc.xmu.edu.cn/index_cn/project/CS_MRI_GraphWavelet_Multicontrast/Toolbox_GBRWT_Multicontrast_MRI.zip
)
联系人: 屈小波 quxiaobo<|at|>xmu.edu.cn
摘要:
随着磁共振应用的广泛应用,在保证磁共振图像质量的前提下加速磁共振成像速度非常重要。通过欠采样的k空间数据并结合稀疏重建能有效的加快磁共振的成像速度。然而,欠采率太高会导致图像细节丢失、图像模糊。为了进一步提高欠采率并加快成像速度,我们利用磁共振成像通常一次成像过程需要采集多对比度图像的特点,以其中一种对比度的图像作为参考图像,训练自适应于当前成像目标的graph稀疏表示。稀疏表示的能力越强,稀疏重建的图像质量越好,从而能降低采样率、加快成像速度。同时,考虑到多对比度图像之间的不配准问题会减弱参考图像训练的稀疏表示对重建目标的实用性,我们构建了图像配准与稀疏重建的二次规划模型。实验结果表明,相同采样率下,本文方法相对于其他方法能得到更好的重建图像质量。同时,由于考虑了图像配准,本文方法对成像目标有一定运动的情况下也有一定的鲁棒性。
关键词: 磁共振成像,图像重建,稀疏表示, 多对比度,图像配准
方法:
本文方法主要包含两个部分,一是多对比度图像配准,用于训练graph稀疏表示的全采样参考图像要先配准到待重建的目标图像上,以保证训练得到的稀疏表示能自适应于目标图像的稀疏重建。二是稀疏训练及稀疏重建, 利用参考图像(多对比度图像)的图像块构建加权的graph结构,其中每个图像块为顶点、图像块之间的相似性为权重,通过最短路径访问找到图像像素的光滑排序,构成本文的graph稀疏表示(multi-contrast
image guided graph-based redundant wavelet transform, MGBRWT)。最后,利用MGBRWT稀疏表示做目标图像的稀疏重建。图像配准及目标图像的稀疏重建被构建成一个二次规划模型,通过配准与稀疏的迭代求解得到重建图像的最优化结果。本文方法的实验流程如图1所示。
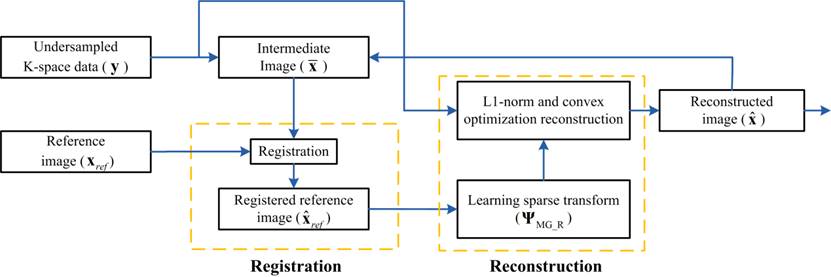
Fig.
1 Flowchart of this work.
实验结果:
1.活体数据的多对比度图像稀疏重建结果对比。.
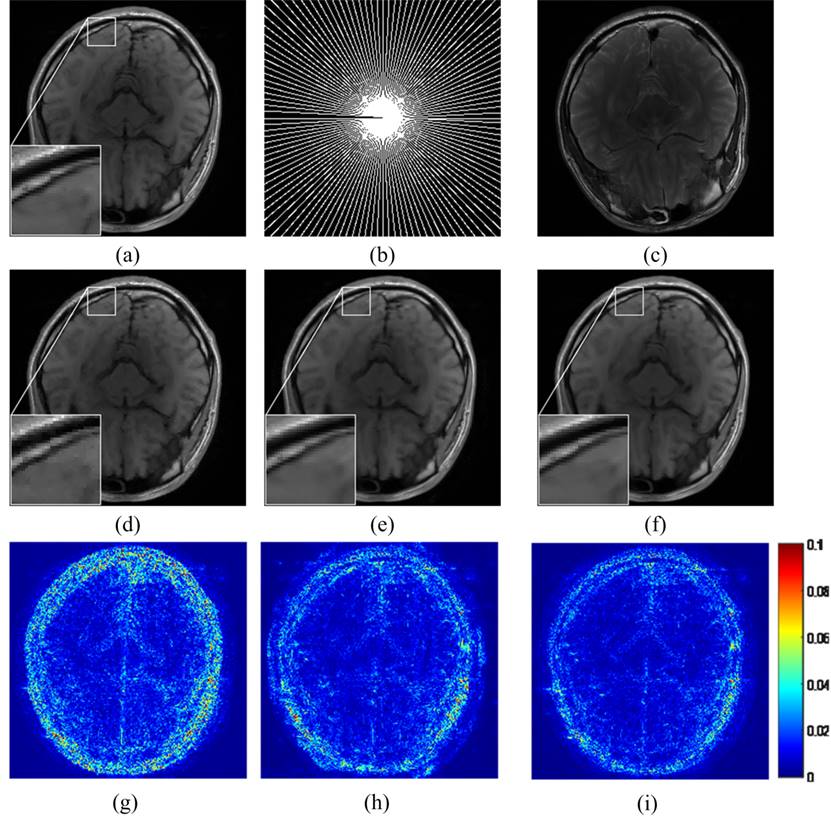
Fig. 2 MRI reconstruction with pseudo radial sampling.
The (a-c) are the ground-truth, pseudo radial under-sampling with 25% data, and reference, respectively. (d-f) are the
reconstructed images using BCS[42,43], PANO[41] and the proposed method; (g-i) magnitude errors using BCS, PANO and the proposed
method. Note: (d-f)
achieved RLNEs 0.071, 0.056 and 0.048, respectively; (d-f) achieved MSSIMs
0.9508, 0.9581 and 0.9673, respectively.
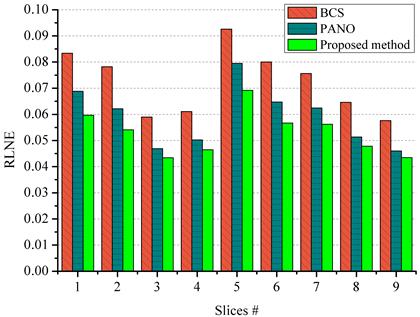
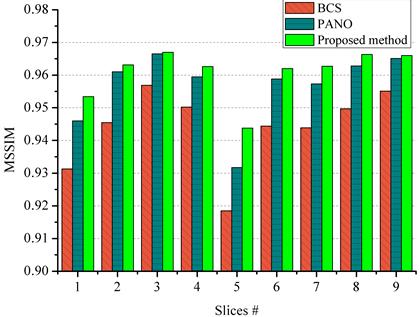
Fig. 3
Reconstruction with more MRI slices. The (a) and (b) are reconstructed RLNEs
and MSSIMs with 20% under-sampled data.
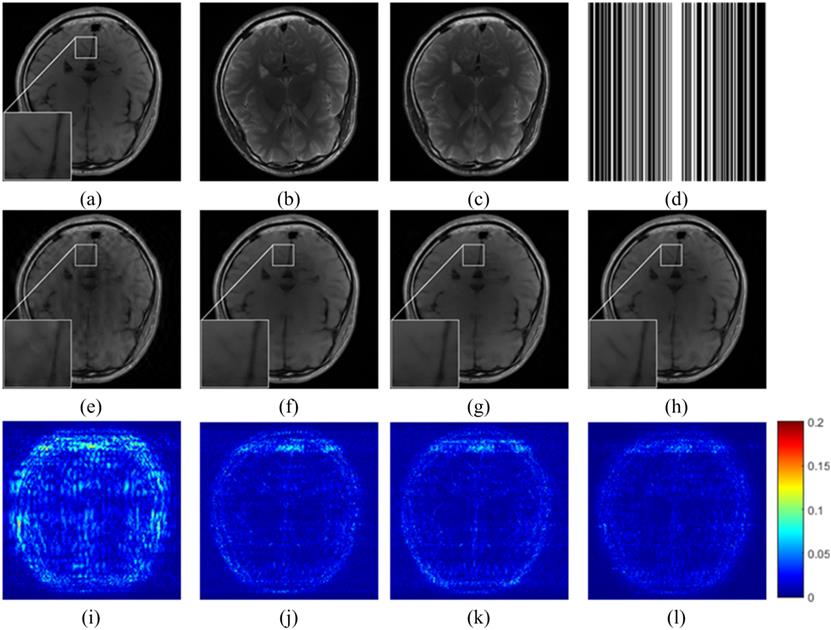
Fig.
4 Reconstructed images using other typical methods. (a) The fully sampled
target image; (b) is the unregistered reference image in another contrast; (c)
is the registered reference image; (d) denotes the under-sampling pattern;
(e-h) are reconstructed images using the l 21-norm[48],
TLMRI[15], DLMRI[9] and the proposed method with the registered another
contrast image in (c) as the reference image. (i-l) are reconstructed errors of
l 21-norm,
TLMRI, DLMRI reconstructions and the proposed method.
2. 多对比度图像作为参考图像相对于无参考图像的优势
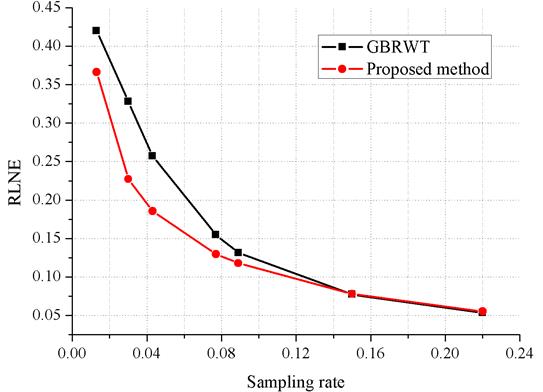
Fig. 5 Proposed
method vs. original GBRWT-based MRI reconstruction[16]. The target and
reference images are same with that shown in Fig. 2 in the full paper.
结论:
本文构建了一种结合多对比度图像为参考图像的磁共振图像稀疏重建方法。通过从参考图像学习graph稀疏表示用以目标图像的欠采样重建,并且通过迭代优化多对比度图像的配准及稀疏重建来实现多对比度图像稀疏重建的最优化。实验结果表明,当采样率很低时,多对比度图像作为参考图像能改善稀疏重建的结果,此研究对加速磁共振成像是有意义的。同时,多对比度图像配准及稀疏重建的迭代优化使得本文方法对实验条件要求降低,允许成像目标有一定的运动的情况下的磁共振成像。
参考文献
[1] H. Jung, K. Sung, K.
S. Nayak, E. Y. Kim, and J. C. Ye, "k-t FOCUSS: a general compressed sensing
framework for high resolution dynamic MRI," Magn Reson Med. 61 (2009) 103-16.
[2] T.
Zhang, J. Y. Cheng, A. G. Potnick, R. A. Barth, M. T. Alley, M. Uecker, et al.,
"Fast pediatric 3D free-breathing abdominal dynamic contrast enhanced MRI
with high spatiotemporal resolution," J
Magn Reson Imaging, 41 (2015), 460-73.
[3] Y.
Hu and G. H. Glover, "Increasing spatial coverage for high-resolution
functional MRI," Magn. Reson. Med., 61 (2009), 716-722.
[4] M.
Lustig, D. Donoho, and J. M. Pauly, "Sparse MRI: The application of
compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging," Magn. Reson. Med. 58 (2007)
1182-95.
[5] M.
Lustig, D. L. Donoho, J. M.Santos, and J. M. Pauly, "Compressed sensing
MRI," IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 72 (2008) 72-82.
[6] Y.
Yang, F. Liu, W. Xu, and S. Crozier, "Compressed sensing MRI via two-stage
reconstruction," IEEE Trans. Bio-Med
Eng. 62 (2015) 110-118.
[7] S.
G. Lingala and M. Jacob, "Blind compressive sensing dynamic MRI," IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32 (2013)
1132-1145.
[8] X.
Ye, Y. Chen, and F. Huang, "Computational acceleration for MR image
reconstruction in partially parallel imaging," IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30 (2011) 1055-1063.
[9] S.
Ravishankar and Y. Bresler, "MR image reconstruction from highly
undersampled k-space data by dictionary learning," IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30 (2011) 1028-1041.
[10] X.
Qu, D. Guo, B. Ning, Y. Hou, Y. Lin, S. Cai,
et al., "Undersampled MRI reconstruction with patch-based directional
wavelets,"Magn.
Reson. Imaging 30 (2012)
964-977.
[11] Z.
Zhan, J. F. Cai, D. Guo, Y. Liu, Z. Chen, and X. Qu, "Fast multiclass
dictionaries learning wth geometrical directions in MRI reconstruction," IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 63 (2016)
1850-1861.
[12] Q.
Liu, S. Wang, K. Yang, J. Luo, Y. Zhu, and D. Liang, "Highly undersampled
magnetic resonance image reconstruction using two-Level Bregman method with
dictionary updating," IEEE Trans.
Med. Imaging 32 (2013) 1290-1301.
[13] A.
Majumdar, "Motion predicted online dynamic MRI reconstruction from
partially sampled k-space data,"Magn.
Reson Imaging 31 (2013) 1578-1586.
[14] R. W.
Liu, L. Shi, W. Huang, J. Xu, S. C. H. Yu, and D. Wang, "Generalized total
variation-based MRI Rician denoising model with spatially adaptive
regularization parameters,"Magn.
Reson Imaging 32 (2014) 702-720.
[15] S.
Ravishankar and Y. Bresler, "Efficient Blind Compressed Sensing Using
Sparsifying Transforms with Convergence Guarantees and Application to
MRI," Mathematics, 2 (2015),
294-309.
[16] Z.
Lai, X. Qu, Y. Liu, D. Guo, J. Ye, Z. Zhan, and Z. Chen, "Image
reconstruction of compressed sensing MRI using graph-based redundant wavelet
transform," Med. Image Anal. 27
(2016) 93-104.
[17] B. M.
Dale, M. A. Brown, and R. C. Semelka, "Principles of magnetic resonance
imaging," in MRI BasicPrinciples
AndApplications, Ed: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, (2015) 26-38.
[18] A.
Menini, G. S. Slavin, J. A. Stainsby, P. Ferry, J. Felblinger, and F. Odille,
"Motion correction of multi-contrast images applied to T1 and T2
quantification in cardiac MRI," Magn.
Reson. Mater. Phy. 28 (2015) 1-12.
[19] J.
Huang, C. Chen, and L. Axel, "Fast multi-contrast MRI
reconstruction," Magn. Reson.
Imaging 32 (2014) 1344-1352.
[20] A.
Majumdar and R. K. Ward, "Accelerating multi-echo T2 weighted MR imaging:
Analysis prior group-sparse optimization," J. Magn. Reson. 210 (2011) 90-97.
[21] H. Du
and F. Lam, "Compressed sensing MR image reconstruction using a
motion-compensated reference," Magn.
Reson Imaging. 30
(2012). 954-963.
[22] J.
Jin, F. Liu, and S. Crozier, "Image registration guided, sparsity
constrained reconstructions for dynamic MRI," Magn. Reson Imaging 32 (2014). 1403-1417.
[23] I.
Ram, M. Elad, and I. Cohen, "Redundant wavelets on graphs and high
dimensional data clouds," IEEE
Signal Proc. Let. 19 (2012) 291-294.
[24] B.
Yang and S. Li, "Pixel-level image fusion with simultaneous orthogonal
matching pursuit," Inform. Fusion 13
(2012) 10-19.
[25] F. P.
M. Oliveira and J. M. R. S. Tavares, "Medical image registration: a
review," Comput.Method. Bio-Mec. 17
(2014) 73-93.
[26] S.
Li, X. Kang, L. Fang, J. Hu, and H. Yin, "Pixel-level image fusion: a
survey of the state of the art," Inform.
Fusion, 33 (2017) 100-112.
[27] A. P.
James and B. V. Dasarathy, "Medical image fusion: a survey of the state of
the art," Inform. Fusion, 19
(2014) 4-19.
[28] H.
Ghassemian, "A review of remote sensing image fusion methods," Inform. FusionPart A 32 (2016) 75-89.
[29] L.
Tang, G. Hamarneh, and K. Iniewski, "Medical image registration: a
review," Medical Imaging: Technology
and Applications (2013) 619-660.
[30] P. J.
Kostelec and S. Periaswamy, "Image registration for MRI," Modern Signal Processing 46 (2003)
161-185.
[31] P.
Viola and W. M. Wells, "Alignment by maximization of mutual
information," In:Proceedings of the 5th international conference
on computer vision-ICCV (1995) 16-23.
[32] J. P.
W. Pluim, J. B. A. Maintz, and M. A. Viergever, "Mutual-information-based
registration of medical images: a survey," IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 22 (2003) 986-1004.
[33] D.
Mattes, D. R. Haynor, H. Vesselle, T. K. Lewellen, and W. Eubank,
"Nonrigid multimodality image registration," SPIE, 4322 (2001) 1609-1620.
[34] M.
Styner, C. Brechbuehler, G. Székely, and G. Gerig, "Parametric estimate of
intensity inhomogeneities applied to MRI," IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 19, (2000) 153-165.
[35] Y.
Liu, J. F. Cai, Z. Zhan, D. Guo, J. Ye, Z. Chen, and X. Qu, "Balanced
sparse model for tight frames in compressed sensing magnetic resonance
imaging," PloS One 10 (2015)
547-562.
[36] S.
Boyd, N. Parikh, E. Chu, B. Peleato, and J. Eckstein, "Distributed
optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of
multipliers," Foundations and
Trends® in Machine Learning 3 (2011) 1-122.
[37] M. V.
Afonso, J. M. Bioucas-Dias, and M. A. T. Figueiredo, "Fast image recovery
using variable splitting and constrained optimization," IEEE Trans. Image Proc.19 (2010)
2345-2356.
[38] D. S.
Weller, S. Ramani, and J. A. Fessler, "Augmented lagrangian with variable
splitting for faster non-Cartesian-SPIRiT MR image reconstruction," IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33 (2014)
351-361.
[39] J.
Yang, Y. Zhang, and W. Yin, "A fast alternating direction method for
TVL1-L2 signal reconstruction from partial fourier data," IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 4
(2010) 288-297.
[40] Y.
Liu, Z. Zhan, J. F. Cai, D. Guo, Z. Chen, and X. Qu, "Projected iterative
soft-thresholding algorithm for tight frames in compressed sensing magnetic
resonance imaging," IEEE Trans. Med.
Imaging 35 (2016) 2130-2140.
[41] X. Qu,
Y. Hou, F. Lam, D. Guo, J. Zhong, and Z. Chen, "Magnetic resonance image
reconstruction from undersampled measurements using a patch-based nonlocal
operator," Med. Image Anal. 18
(2014) 843-856.
[42] B.
Bilgic, V. K. Goyal, and E. Adalsteinsson, "Multi-contrast reconstruction
with Bayesian compressed sensing," Magn. Reson. Med. 66 (2011) 1601-15.
[43] B.
Bilgic and E. Adalsteinsson, "Joint Bayesian compressed sensing with prior
estimate," In:Proceedings of the 20thinternational society for
magnetic resonance in medicine – ISMRM’12 (2012) 75.
[44] W.
Zhou, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh, and E. P. Simoncelli, "Image quality
assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity," IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 13 (2004)
600-612.
[45] B.
Ning, X. Qu, D. Guo, C. Hu, and Z. Chen, "Magnetic resonance image
reconstruction using trained geometric directions in 2D redundant wavelets
domain and non-convex optimization," Magn
Reson. Imaging 31 (2013) 1611-1622.
[46] B. R,
Choi H., Neelamani R., RibeiroV., Romberg J., Guo H., et. al., "Rice
wavelet toolbox," 2009.
[47] M. H.
Kayvanrad, A. J. McLeod, J. S. H. Baxter, C. A. McKenzie, and T. M. Peters,
"Stationary wavelet transform for under-sampled MRI reconstruction," Magn. Reson Imaging 32 (2014) 1353-1364.
[48] A.
Majumdar and R. K. Ward, "Joint reconstruction of multiecho MR images
using correlated sparsity," Magn.
Reson Imaging, 29 (2011), 899-906.