Review and Prospect: Deep Learning in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Dicheng Chen1,#, Zi Wang1,#, Di Guo2, Vladislav Orekhov3, Xiaobo Qu1,*
1 Department of Electronic Science, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Plasma and Magnetic Resonance, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 School of Computer and Information Engineering, Xiamen University of Technology, Xiamen 361024, China
3 Department of Chemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Gothenburg, Box 465, Gothenburg 40530, Sweden
* Email:quxiaobo <at> xmu.edu.cn or quxiaobo2009 <at> gmail.com
# Co-first authorship
Citation
Dicheng Chen#, Zi Wang#, Di Guo, Vladislav Orekhov, Xiaobo Qu*. Review and Prospect: Deep Learning in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Chemistry -A European Journal, DOI: 10.1002/chem.202000246, 2020.
Link
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/chem.202000246
Synopsis
Deep Learning (DL) can discover fruitful features embedded in large data sets and figure out the complex nonlinear mapping between inputs and outputs without prior knowledge. In view of the clear success, researchers in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) field start to pay attention to DL and explore it for addressing deficiencies of conventional methods. In this paper, we systematically summarize applications of DL in NMR spectroscopy including spectra reconstruction, denoising, chemical shift prediction and automated peak picking.
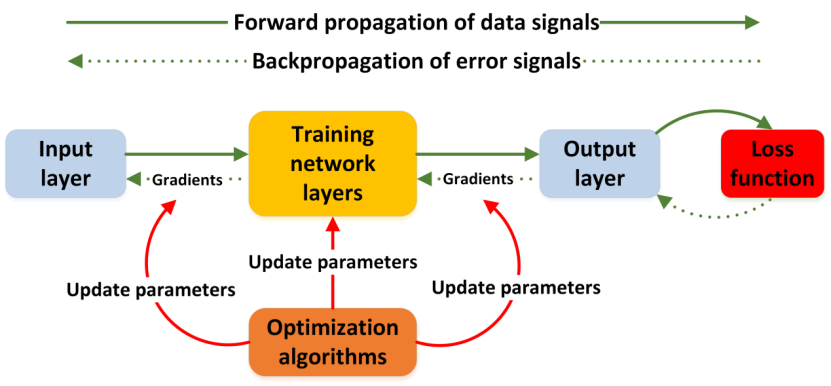
Figure 1. The flowchart of neural network training.
Main content
Firstly, we introduce two methods for fast reconstructing high-quality spectra from undersampled data, which use Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network trained by synthetic NMR data, respectively. Their reconstruction performances are comparable with the state-of-the-art iterative methods, but they show outstanding advantages in computational time.
Secondly, in denoising, we mention a CNN trained by simulation data, which can infer the mapping between the spectra with lots of interference and the high Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) spectra. Its robust performance for low SNR may promote the development of clinical applications.
Thirdly, researchers used different neural networks to create relationships between the information of compounds and their chemical shifts. The results show that, these networks can apparently approach the limits of empirical methods for predicting chemical shift and the accuracy is comparable to the ab initio quantum chemistry methods.
Finally, DL is demonstrated to be used for automated peak picking, and we focus on two networks. One is called NMR-Net, the other is trained by simulated spectra with labels. The result on realistic data shows that, their picking accuracies are consistent with the manually selected signal regions.
Furthermore, we outline a perspective for DL as entirely new approaches that is likely to transform NMR spectroscopy into a much more efficient and powerful technique in chemistry and life science.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under grants 61971361, 61871341, and U1632274, the Joint NSFC-Swedish Foundation for International Cooperation in Research and Higher Education (STINT) under grant 61811530021, the National Key R&D Program of China under grant 2017YFC0108703, the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China under grant 2018J06018, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under grant 20720180056, the Xiamen University Nanqiang Outstanding Talents Program, the Science and Technology Program of Xiamen under grant 3502Z20183053, the Swedish Research Council under grant 2015–04614, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research under grant ITM17-0218.
Reference
[1] a) B. R. Kowalski, C. F. Bender, Anal. Chem. 1972, 44, 1405-1411; b) K. Esbensen, P. Geladi, J. Chemometr. 1990, 4, 389-412.
[2] Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, G. Hinton, Nature 2015, 521, 436.
[3] a) S. Wang, Z. Su, L. Ying, X. Peng, S. Zhu, F. Liang, D. Feng, D. Liang, in 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2016, pp. 514-517; b) C. Cai, C. Wang, Y. Zeng, S. Cai, D. Liang, Y. Wu, Z. Chen, X. Ding, J. Zhong, Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 2202-2214; c) J. Schlemper, J. Caballero, J. V. Hajnal, A. N. Price, D. Rueckert, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 491-503; d) Y. Yang, J. Sun, L. I. H, Z. Xu, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. and Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 521-538.
[4] a) X. Qu, Y. Huang, H. Lu, T. Qiu, D. Guo, T. Agback, V. Orekhov, Z. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201908162; b) D. F. Hansen, J. Biomol. NMR 2019, 73, 577-585.
[5] P. Klukowski, M. Augoff, M. Zięba, M. Drwal, A. Gonczarek, M. J. Walczak, Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2590-2597.
[6] D. Svozil, V. Kvasnicka, J. í. Pospichal, Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 1997, 39, 43-62.
[7] a) Y. Lecun, B. Boser, J. Denker, D. Henderson, R. E. Howard, W. Hubbard, L. Jackel, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 1990; b) S. Lawrence, C. Giles, A. Tsoi, A. Back, IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 1997, 8, 98-113; c) A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G. Hinton, in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) 2012.
[8] a) Y. Bengio, P. Simard, P. Frasconi, IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 1994, 5, 157-166; b) R. Williams, D. Zipser, Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 270-280; c) S. Hochreiter, J. Schmidhuber, Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735-1780.
[9] N. Hecht, in International 1989 Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 1989, pp. 593-605.
[10] L. Bottou, P. Neuro-Nımes, 1991, 91.
[11] D. Kingma, J. Ba, Computer Science 2014.
[12] N. Srivastava, G. Hinton, A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, R. Salakhutdinov, J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929-1958.
[13] S. Ioffe, C. Szegedy, Computer Science 2015.
[14] V. Nair, G. Hinton, Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML10), 2010, 27, 807–814.
[15] S. Min, B. Lee, S. Yoon, Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 18, 851-869.
[16] M. Abadi, A. Agarwal, P. Barham, E. Brevdo, Z. Chen, C. Citro, G. s. Corrado, A. Davis, J. Dean, M. Devin, S. Ghemawat, I. Goodfellow, A. Harp, G. Irving, M. Isard, Y. Jia, R. Jozefowicz, L. Kaiser, M. Kudlur, X. Zheng, arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.04467 2016.
[17] R. Collobert, K. Kavukcuoglu, C. Farabet, in BigLearn, Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) Workshop, 2011.
[18] Y. Jia, E. Shelhamer, J. Donahue, S. Karayev, J. Long, R. Girshick, S. Guadarrama, T. Darrell, Computer Science 2014.
[19] MathWorks, MATLAB Deep Learning Toolbox 2019, URL: https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html.
[20] H. Lee, H. Kim, Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 33-48.
[21] Y. Shen, A. Bax, J. Biomol. NMR 2010, 48, 13-22.
[22] a) Y. Shen, A. J. J. o. B. N. Bax, J. Biomol. NMR 2013, 56, 227-241; b) Y. Shen, A. Bax, Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.) 2015, 1260, 17-32.
[23] F. H. Allen, V. J. Hoy, in International Tables for Crystallography Volume F: Crystallography ofbiological macromolecules (Eds.: M. G. Rossmann, E. Arnold), Springer, Dordrecht, 2001, pp. 663-668.
[24] S. Liu, J. Li, K. Bennett, B. Ganoe, T. Stauch, M. Head-Gordon, A. Hexemer, D. Ushizima, T. Head-Gordon, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 4558-4565.
[25] P. Klukowski, A. Gonczarek, M. J. Walczak, in 2015 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), 2015, pp. 1-8.
[26] Bruker Biospin Corporation, in European Magnetic Resonance Meeting, 2019, URL: https://www.bruker.com/fileadmin/user_upload/5-Events/2019/BBIO/EUROISMAR/Deep-Learning-Applications-in-NMR-low-res.pdf.
[27] J. C. J. Barna, E. D. Laue, M. R. Mayger, J. Skilling, S. J. P. Worrall, J. Magn. Reson. 1987, 73, 69-77.
[28] a) V. Jaravine, I. Ibraghimov, V. Yu Orekhov, Nature Methods 2006, 3, 605-607; b) X. Qu, X. Cao, D. Guo, Z. Chen, in International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 19th Scientific Meeting, 2010, pp. 3371; c) K. Kazimierczuk, J. Stanek, A. Zawadzka-Kazimierczuk, W. Koźmiński, Prog. Nucl. Mag. Res. Sp. 2010, 57, 420-434; d) K. Kazimierczuk, V. Y. Orekhov, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5556-5559; e) D. J. Holland, M. J. Bostock, L. F. Gladden, D. Nietlispach, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6548-6551; f) X. Qu, D. Guo, X. Cao, S. Cai, Z. Chen, Sensors 2011, 11, 8888-8909; g) S. G. Hyberts, A. G. Milbradt, A. B. Wagner, H. Arthanari, G. Wagner, J Biomol. NMR 2012, 52, 315-327; h) M. Mayzel, K. Kazimierczuk, V. Y. Orekhov, Chem. Commu. 2014, 50, 8947-8950; i) X. Qu, M. Mayzel, J.-F. Cai, Z. Chen, V. Orekhov, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 852-854; j) J. Ying, F. Delaglio, D. A. Torchia, A. Bax, J. Biomol. NMR 2017, 68, 101-118.
[29] a) J. Ying, H. Lu, Q. Wei, J.-F. Cai, D. Guo, J. Wu, Z. Chen, X. Qu, IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2017, 65, 3702-3717; b) D. Guo, H. Lu, X. Qu, IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16033-16039; c) J. Ying, J.-F. Cai, D. Guo, G. Tang, Z. Chen, X. Qu, IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2018, 66, 5520-5533; d) H. Lu, X. Zhang, T. Qiu, J. Yang, J. Ying, D. Guo, Z. Chen, X. Qu, IEEE Trans. on Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 809-820.
[30] S. W. Provencher, Magn. Reson. Med. 1993, 30, 672-679.
[31] a) S. Williams, Prog. Nucl. Mag. Res. Sp. 1999, 35, 201; b) F. Jiru, Eur. J. Radiol. 2008, 67, 202-217.
[32] P. S. Allen, R. B. Thompson, A. H. Wilman, NMR Biomed. 1997, 10, 435-444.
[33] a) P. Luginbühl, T. Szyperski, K. Wüthrich, J. Magn. Reson. 1995, 109, 229-233; b) G. Cornilescu, F. Delaglio, A. Bax, J. Biomol. NMR 1999, 13, 289-302; c) A. Cavalli, X. Salvatella, C. M. Dobson, M. Vendruscolo, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9615-9620; d) Y. Shen, O. Lange, F. Delaglio, P. Rossi, J. Aramini, G. Liu, A. Eletsky, Y. Wu, K. Singarapu, A. Lemak, A. Ignatchenko, C. Arrowsmith, T. Szyperski, G. Montelione, D. Baker, A. Bax, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4685-4690; e) D. Wishart, D. Arndt, M. Berjanskii, P. Tang, J. Zhou, G. Lin, Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 496-502; f) Y. Shen, F. Delaglio, G. Cornilescu, A. Bax, J. Biomol. NMR 2009, 44, 213-223.
[34] S. Neal, A. Nip, H. Zhang, D. Wishart, J. Biomol. NMR 2003, 26, 215-240.
[35] Y. Shen, A. Bax, J. Biomol. NMR 2007, 38, 289-302.
[36] K. Kohlhoff, P. Robustelli, A. Cavalli, X. Salvatella, M. Vendruscolo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13894-13895.
[37] J. Meiler, J. Biomol. NMR 2003, 26, 25-37.
[38] M. Williamson, C. Craven, J. Biomol. NMR 2009, 43, 131-143.
[39] G. J. Kleywegt, R. Boelens, R. Kaptein, J. Magn. Reson. 1990, 88, 601-608.
[40] B. A. Johnson, in Protein NMR Techniques (Ed.: A. K. Downing), Humana Press, NJ, 2004, pp. 313-352.
[41] C. Bartels, T.-h. Xia, M. Billeter, P. Güntert, K. Wüthrich, J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 6, 1-10.
[42] S. P. Skinner, R. H. Fogh, W. Boucher, T. J. Ragan, L. G. Mureddu, G. W. Vuister, J. Biomol. NMR 2016, 66, 111-124.
[43] Z. Liu, A. Abbas, B.-Y. Jing, X. Gao, Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 914-920.
[44] a) B. Alipanahi, X. Gao, E. Karakoc, L. Donaldson, M. Li, Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 268-275; b) S. Tikole, V. Jaravine, V. Rogov, V. Dötsch, P. Güntert, BMC Bioinformatics 2014, 15, 46.
[45] a) Y. Cheng, X. Gao, F. Liang, Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2014, 12, 39-47; b) J. M. Würz, P. Güntert, J. Biomol. NMR 2017, 67, 63-76.
[46] Y. Bengio, T. Deleu, N. Rahaman, R. Ke, S. Lachapelle, O. Bilaniuk, A. Goyal, C. Pal, arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.10912 2019.
[47] J. Amey, I. Kuprov, arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.01498 2019.
[48] F. Lam, Y. Li, X. Peng, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 545-555.
[49] E. L. Ulrich, H. Akutsu, J. F. Doreleijers, Y. Harano, Y. E. Ioannidis, J. Lin, M. Livny, S. Mading, D. Maziuk, Z. Miller, E. Nakatani, C. F. Schulte, D. E. Tolmie, R. Kent Wenger, H. Yao, J. L. Markley, Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D402-D408.
[50] H. M. Berman, T. N. Bhat, P. E. Bourne, Z. Feng, G. Gilliland, H. Weissig, J. Westbrook, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2000, 7, 957-959.
[51] D. Li, R. Brüschweiler, J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 62, 403-409.
[52] M. Lundborg, G. Widmalm, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1514-1517.
[53] D. Li, R. Brüschweiler, J. Biomol. NMR 2012, 54, 257-265.
[54] NMRbox, 2020, URL: https://nmrbox.org.