Phase-Constrained Reconstruction of High-Resolution Multi-shot
Diffusion Weighted Image ( [English] )
黄以满1, 张心林1, 郭华2, 陈慧军2, 郭迪3, 黄峰4, 许勤4, 屈小波1*
1厦门大学,电子科学系,福建等离子体与磁共振重点研究实验室,中国,厦门;
2清华大学,生物医学工程系,生物医学成像研究中心,中国,北京;
3厦门理工学院,计算机与信息工程学院,中国,厦门;
4东软医疗系统有限公司,中国,上海.
联系人:
quxiaobo<|at|>xmu.edu.cn
引用: Yiman Huang, Xinlin Zhang, Hua Guo,
Huijun Chen, Di Guo, Feng Huang, Qin Xu, Xiaobo Qu*, Phase-constrained
reconstruction of high-resolution multi-shot diffusion weighted magnetic
resonance image, Journal of Magnetic Resonance, DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2020.106690,
2020.
全文链接:https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1aZ%7EG3u0yjN80o
摘要:
扩散加权成像(Diffusion
weighted imaging , DWI)是肿瘤诊断和急性中风评估中的独特检查方法。单激发平面回波成像是目前用于扩散加权成像的常规方法。但是,单激发成像有图像失真,模糊和低空间分辨率的缺点。尽管多激发扩散加权成像提高了图像分辨率,但它同时带来了不同次激发之间的相位变化。我们通过强加从k空间数据构造的汉克尔矩阵的低秩性,将多激发图像的平滑相位约束引入到多激发无导航DWI图像重建中。此外,我们利用部分奇异值最小化方法来约束汉克尔矩阵的低秩。脑部成像数据的结果表明,在去除伪影方面,所提出的方法优于最新的重建方法,并且我们的方法潜在地具有重建高激发数DWI的能力。
关键词:
扩散加权成像,汉克尔矩阵,图像重建,低秩,磁共振成像。
方法:
1.
背景
扩散加权磁共振成像(MRI)是在生物医学成像中无创地检测组织中水分子的布朗运动的一种独特的检查方法。它被广泛用于肿瘤诊断,急性中风评估和神经科学研究。作为常规的扩散加权成像(DWI)方法,单激发平面回波成像(echo-planar imaging , EPI)具有运动抗扰性和采集时间短的优点,但存在图像失真,模糊和空间分辨率低的问题。一些抵抗DWI失真的方法被提出来,例如时空编码和多激发EPI。
多激发交错式EPI通过对每次激发中的不同片段进行采样来完全获取k空间数据,如图1所示。多激发EPI提供的空间分辨率高于单激发EPI。但是,多激发成像对生理运动敏感,会导致每次激发所采集的数据相位不一致。将多激发数据直接合成完全采样的k空间中将导致图像中出现严重伪影。
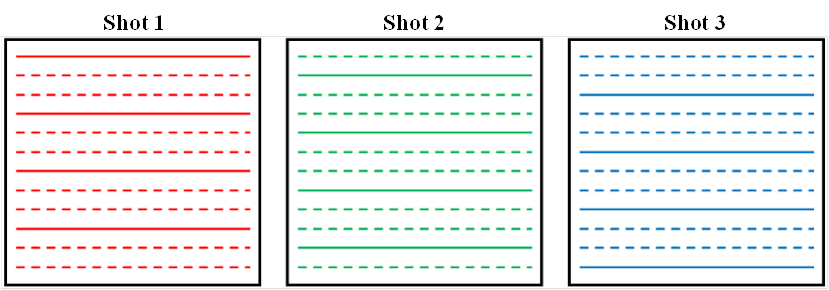
图1. 3激发交错式DWI采样示意图。注意:实线表示图像的k空间(傅立叶空间)中的采到的数据点,虚线表示未采到信号的数据点。
2.
约束相位的低秩汉克尔矩阵重建
我们利用部分奇异值之和的方法来约束低秩性,所提出的秩最小化模型如下:
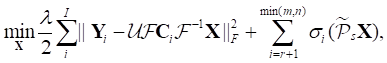
其中 ![]() 表示多激发k空间数据的级联矩阵,
表示多激发k空间数据的级联矩阵,
![]() ,
,
![]() 是将
是将 ![]() 转化成LORAKS中的
转化成LORAKS中的![]() 矩阵的算子,
矩阵的算子,![]() 是傅里叶变换算子,
是傅里叶变换算子, ![]() 是反傅里叶变换算子,
是反傅里叶变换算子, ![]() 是第i个通道的灵敏度矩阵,
是第i个通道的灵敏度矩阵,
![]() 对k空间数据进行采样,并对非采样数据点(通道采样k空间数据)进行填零操作的算子,
对k空间数据进行采样,并对非采样数据点(通道采样k空间数据)进行填零操作的算子, ![]() 第i个通道中采样道德数据,
第i个通道中采样道德数据,
![]() 是矩阵
是矩阵![]() 的秩,
的秩, ![]() 是矩阵
是矩阵![]() 的行数和列数,
的行数和列数, ![]() 是权衡数据一致性和低秩约束的正则化参数。
是权衡数据一致性和低秩约束的正则化参数。
3.
主要结果
我们将所提出的方法与两种最新的无导航DWI图像重建方法进行了比较,包括POCS-ICE和MUSSELS。图2显示了8次激发DWI的两个层的重建。图2(d)显示了由IRIS重建的参考图。如红色箭头所示,轻微的伪影仍保留在POCS-ICE的重建结果中(图2(a))。POCS-MUSSELS重建图像(图2(b))未显示明显的伪像,但图像中心看起来很暗,如黄色箭头所示。而我们的结果(图2(c))可以有效地重建图像,但伪像最少。
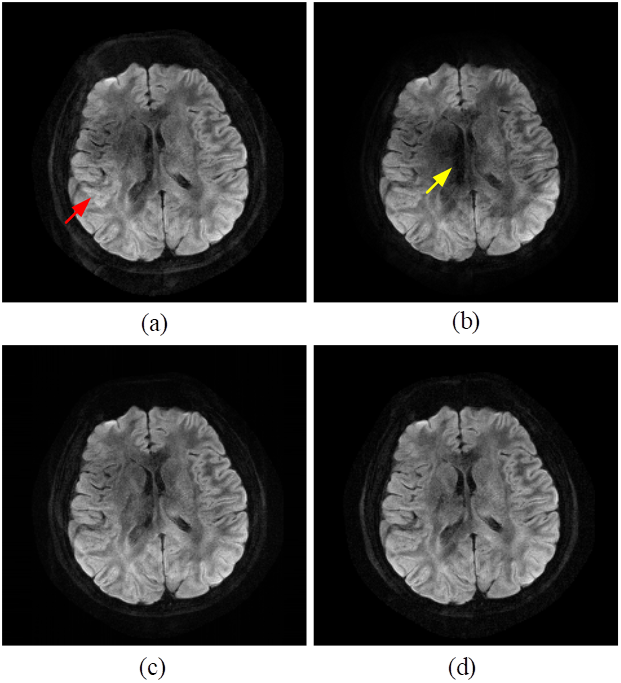
图2. 使用不同的重建方法重建8头部DWI的第9层。(a)POCS-ICE,(b)POCS-MUSSELS,(c)提出的方法,(d)由IRIS重建的参考图。残留伪影用红色箭头标记,较暗区域用黄色箭头标记。
图3显示了3层12次激发DWI的重建图像。直接逆傅立叶变换的图像会有严重的混叠伪像(图3(a))。
POCS-ICE无法消除严重的混叠伪像(图3(b))。POCS-MUSSELS在某种程度上去除了伪影,但是图像中仍然保留了少量伪影(图3(c))。
而所提出的方法可以比POCS-MUSSELS更有效地重建出具有最少伪像和锐利边缘的图像,如图3(d)所示。
这个实验,是重建了很激进的高激发数的,高达12次激发。POCS-ICE和POCS-MUSSELS难以恢复无伪像的图像,而所提出的方法具有处理高激发数DWI的潜力。
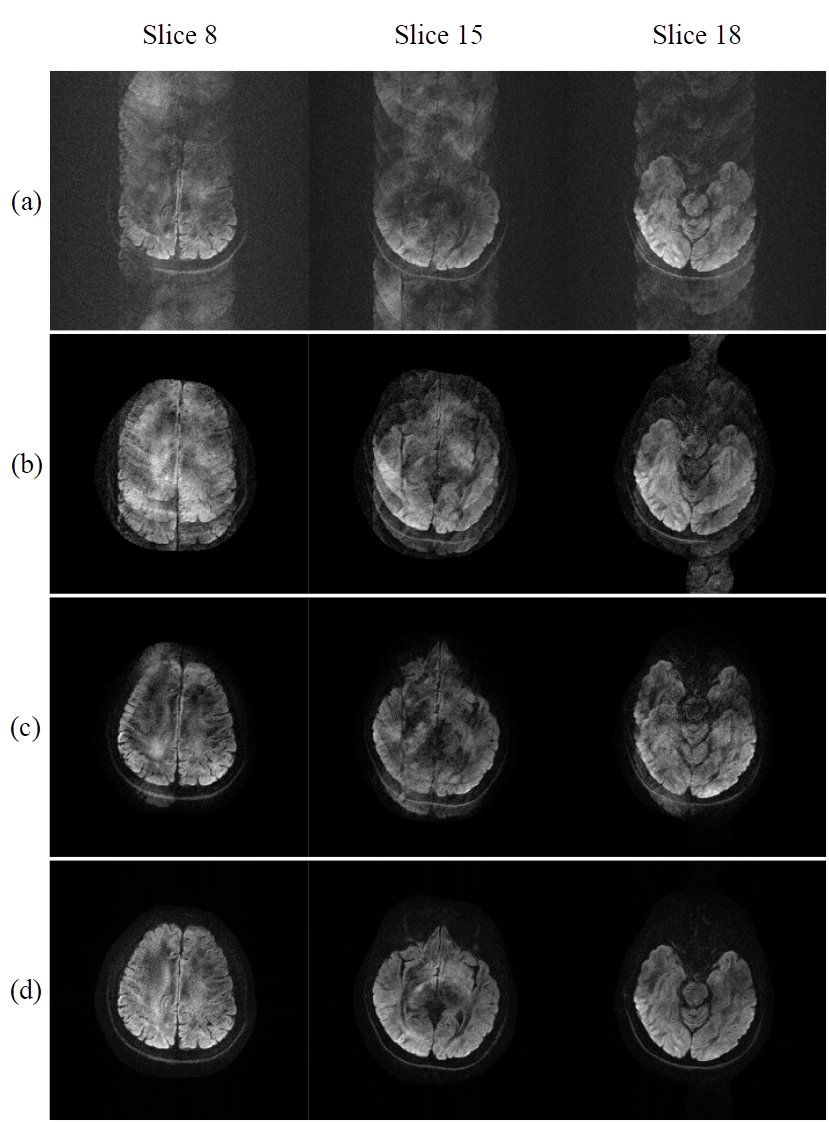
图3. 使用不同的重建方法重建3层12激发头部DWI。(a)未经校正的直接重建,(b)POCS-ICE,(c)POCS-MUSSELS,(d)所提出的方法。
致谢:
这项工作得到了国家重点研发计划(2017YFC0108700),国家自然科学基金(61971361、61871341、61811530021和61672335),福建省自然科学基金(2018J06018),中央高校基本科研基金(20720180056),厦门市科学技术计划(3502Z20183053)和中国奖学金委员会资助。
作者要感谢联影公司的李国斌博士提供了12激发头部DWI数据。
参考文献:
[1] D.
Le Bihan, E. Breton, D. Lallemand, P. Grenier, E. Cabanis, and M.
Laval-Jeantet, "MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application
to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders," Radiology, vol. 161, no. 2, pp. 401-407, 1986.
[2] D.
Le Bihan, J. F. Mangin, C. Poupon, C. A. Clark, S. Pappata, N. Molko, and H.
Chabriat, "Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications," Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, vol.
13, no. 4, pp. 534-546, 2001.
[3] S.
Mori and J. Zhang, "Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its
applications to basic neuroscience research," Neuron, vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 527-539, 2006.
[4] A.
G. Sorensen, F. S. Buonanno, R. G. Gonzalez, L. H. Schwamm, M. H. Lev, F. R.
Huang-Hellinger, T. G. Reese, R. M. Weisskoff, T. L. Davis, and N. Suwanwela,
"Hyperacute stroke: evaluation with combined multisection
diffusion-weighted and hemodynamically weighted echo-planar MR imaging," Radiology, vol. 199, no. 2, pp. 391-401,
1996.
[5] M.
D. Budde and N. P. Skinner, "Diffusion MRI in acute nervous system
injury," Journal of Magnetic
Resonance, vol. 292, pp. 137-148, 2018.
[6] F.
Farzaneh, S. J. Riederer, and N. J. Pelc, "Analysis of T2 limitations and
off-resonance effects on spatial resolution and artifacts in echo-planar
imaging," Magnetic Resonance in
Medicine, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 123-139, 1990.
[7] E.
Solomon, N. Shemesh, and L. Frydman, "Diffusion weighted MRI by
spatiotemporal encoding: analytical description and in vivo validations," Journal of Magnetic Resonance, vol. 232,
pp. 76-86, 2013.
[8] H.
K. Jeong, J. C. Gore, and A. W. Anderson, "High-resolution human diffusion
tensor imaging using 2-D navigated multishot SENSE EPI at 7 T," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 69,
no. 3, pp. 793-802, 2013.
[9] X.
Ma, Z. Zhang, E. Dai, and H. Guo, "Improved multi-shot diffusion imaging
using GRAPPA with a compact kernel," Neuroimage,
vol. 138, pp. 88-99, 2016.
[10] N.
K. Chen, A. Guidon, H. C. Chang, and A. W. Song, "A robust multi-shot scan
strategy for high-resolution diffusion weighted MRI enabled by multiplexed
sensitivity-encoding (MUSE)," Neuroimage,
vol. 72, no. 2, pp. 41-47, 2013.
[11] H.
Guo, X. Ma, Z. Zhang, B. Zhang, C. Yuan, and F. Huang, "POCS‐enhanced
inherent correction of motion‐induced phase errors (POCS‐ICE) for
high‐resolution multishot diffusion MRI," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 75, no. 1, pp. 169-180, 2016.
[12] M.
Mani, M. Jacob, D. Kelley, and V. Magnotta, "Multi‐shot
sensitivity‐encoded diffusion data recovery using structured low‐rank matrix
completion (MUSSELS)," Magnetic
Resonance in Medicine, vol. 78, no. 2, pp. 494-507, 2017.
[13] Y.
Hu, E. G. Levine, Q. Tian, C. J. Moran, X. Wang, V. Taviani, S. S. Vasanawala,
J. A. McNab, B. A. Daniel, and B. L. Hargreaves, "Motion‐robust
reconstruction of multishot diffusion‐weighted images without phase estimation
through locally low‐rank regularization," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 81, no. 2, pp. 1181-1190,
2019.
[14] L.
Guo, F. Huang, Z. Xu, Y. Mei, W. Fang, X. Ma, E. Dai, H. Guo, Q. Feng, and W.
Chen, "eIRIS: Eigen-analysis approach for improved spine multi-shot
diffusion MRI," Magnetic Resonance
Imaging, vol. 50, pp. 134-140, 2018.
[15] W.
Liu, X. Zhao, Y. Ma, X. Tang, and J.-H. Gao, "DWI using navigated
interleaved multishot EPI with realigned GRAPPA reconstruction," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 75,
no. 1, pp. 280-286, 2016.
[16] E.
Dai, Z. Zhang, X. Ma, Z. Dong, X. Li, Y. Xiong, C. Yuan, and H. Guo, "The
effects of navigator distortion and noise level on interleaved EPI DWI
reconstruction: a comparison between image‐and k‐space‐based method," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 80,
no. 5, pp. 2024-2032, 2018.
[17] K.
P. Pruessmann, M. Weiger, M. B. Scheidegger, and P. Boesiger, "SENSE:
sensitivity encoding for fast MRI," Magnetic
Resonance in Medicine, vol. 42, no. 5, pp. 952-962, 1999.
[18] X.
Zhang, D. Guo, Y. Huang, Y. Chen, L. Wang, F. Huang, and X. Qu, "Image
reconstruction with low-rankness and self-consistency of k-space data in
parallel MRI," arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.02846, 2019.
[19] J.
P. Haldar, "Low-rank modeling of local k-space neighborhoods (LORAKS) for
constrained MRI," IEEE Transactions
on Medical Imaging, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 668-681, 2013.
[20] K.
H. Jin, D. Lee, and J. C. Ye, "A general framework for compressed sensing
and parallel MRI using annihilating filter based low-rank Hankel matrix," IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, vol.
2, no. 4, pp. 480-495, 2016.
[21] G.
Ongie and M. Jacob, "Off-the-grid recovery of piecewise constant images
from few Fourier samples," SIAM
Journal on Imaging Sciences, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 1004-1041, 2016.
[22] F.
Lam, C. Ma, B. Clifford, C. L. Johnson, and Z. P. Liang, "High‐resolution
1H‐MRSI of the brain using SPICE: data acquisition and image
reconstruction," Magnetic Resonance
in Medicine, vol. 76, no. 4, pp. 1059-1070, 2016.
[23] X.
Qu, M. Mayzel, J. F. Cai, Z. Chen, and V. Orekhov, "Accelerated NMR
spectroscopy with low‐rank reconstruction," Angewandte Chemie International Edition, vol. 54, no. 3, pp.
852-854, 2015.
[24] X.
Qu, Y. Huang, H. Lu, T. Qiu, D. Guo, T. Agback, V. Orekhov, and Z. Chen,
"Accelerated nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with deep learning,"
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, DOI:
10.1002/anie.201908162, 2019.
[25] H.
Lu, X. Zhang, T. Qiu, J. Yang, J. Ying, D. Guo, Z. Chen, and X. Qu, "Low
rank enhanced matrix recovery of hybrid time and frequency data in fast
magnetic resonance spectroscopy," IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 809-820, 2017.
[26] J.
Ying, H. Lu, Q. Wei, J.-F. Cai, D. Guo, J. Wu, Z. Chen, and X. Qu, "Hankel
matrix nuclear norm regularized tensor completion for N-dimensional exponential
signals," IEEE Transactions on
Signal Processing, vol. 65, no. 14, pp. 3702-3717, 2017.
[27] J.
Ying, J.-F. Cai, D. Guo, G. Tang, Z. Chen, and X. Qu, "Vandermonde
factorization of Hankel matrix for complex exponential signal
recovery—Application in fast NMR spectroscopy," IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 66, no. 21, pp.
5520-5533, 2018.
[28] G.
Ongie and M. Jacob, "Recovery of Piecewise Smooth Images from Few Fourier
Samples," In 2015 International
Conference on Sampling Theory and Applications (SampTA), pp. 543-547, 2015.
[29] P.
J. Shin, P. E. Z. Larson, M. A. Ohliger, M. Elad, J. M. Pauly, D. B. Vigneron,
and M. Lustig, "Calibrationless parallel imaging reconstruction based on
structured low-rank matrix completion," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 72, no. 4, pp. 959-970, 2014.
[30] J.
P. Haldar and J. Zhuo, "P-LORAKS: Low-rank modeling of local k-space
neighborhoods with parallel imaging data," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 75, no. 4, pp. 1499-1514.
[31] T.
H. Kim, K. Setsompop, and J. P. Haldar, "LORAKS makes better SENSE:
Phase-constrained partial fourier SENSE reconstruction without phase
calibration," Magnetic Resonance in
Medicine, vol. 77, no. 3, pp. 1021-1035, 2017.
[32] Z.-P.
Liang, "Spatiotemporal imaging with partially separable functions,"
in 2007 4th IEEE International Symposium
on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 2007, pp. 988-991: IEEE.
[33] B.
Zhao, J. P. Haldar, A. G. Christodoulou, and Z.-P. Liang, "Image
reconstruction from highly undersampled (k, t)-space data with joint partial
separability and sparsity constraints," IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 31, no. 9, pp.
1809-1820, 2012.
[34] S.
G. Lingala, Y. Hu, E. DiBella, and M. Jacob, "Accelerated dynamic MRI
exploiting sparsity and low-rank structure: kt SLR," IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 30, no. 5, pp.
1042-1054, 2011.
[35] R.
A. Lobos, T. H. Kim, W. S. Hoge, and J. P. Haldar, "Navigator-free EPI
ghost correction with structured low-rank matrix models: New theory and
methods," IEEE Transactions on
Medical Imaging, vol. 37, no. 11, pp. 2390-2402, 2018.
[36] Z.
Hu, X. Ma, T.-K. Truong, A. W. Song, and H. Guo, "Phase-updated
regularized SENSE for navigator-free multishot diffusion imaging," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 78,
no. 1, pp. 172-181, 2017.
[37] B.
Recht, M. Fazel, and P. A. Parrilo, "Guaranteed minimum-rank solutions of
linear matrix equations via nuclear norm minimization," SIAM Review, vol. 52, no. 3, pp.
471-501, 2010.
[38] Y.
Hu, D. Zhang, J. Ye, X. Li, and X. He, "Fast and accurate matrix
completion via truncated nuclear norm regularization," IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 2117-2130, 2012.
[39] T.-H.
Oh, H. Kim, Y.-W. Tai, J.-C. Bazin, and I. So Kweon, "Partial sum
minimization of singular values in RPCA for low-level vision," in Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Computer Vision, 2013, pp. 145-152.
[40] S.
Boyd, N. Parikh, E. Chu, B. Peleato, and J. Eckstein, "Distributed
optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of
multipliers," Foundations and
Trends® in Machine learning, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 1-122, 2011.
[41] R.
Chandra, S. Eisenstat, and M. Schultz, "Conjugate gradient methods for
partial differential equations," Yale University New Haven, CT, 1978.
[42] T.-H.
Oh, Y. Matsushita, Y.-W. Tai, and I. So Kweon, "Fast randomized singular
value thresholding for nuclear norm minimization," in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, 2015, pp. 4484-4493.
[43] G.
H. Golub and C. F. Van Loan, "Matrix computations," The Johns Hopkins University Press,
Baltimore, USA, 1989.
[44] M.
Uecker, P. Lai, M. J. Murphy, P. Virtue, M. Elad, J. M. Pauly, S. S.
Vasanawala, and M. Lustig, "ESPIRiT—an eigenvalue approach to
autocalibrating parallel MRI: Where SENSE meets GRAPPA," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 71,
no. 3, pp. 990-1001, 2014.
[45] B. Bilgic, I. Chatnuntawech, M. K. Manhard, Q. Tian, C. Liao, S. S. Iyer, S. F. Cauley, S. Y. Huang, J. R. Polimeni, and L. L. Wald, "Highly accelerated multishot echo planar imaging through synergistic machine learning and joint reconstruction," Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 82, pp. 1343-1358, 2019.